[ad_1]
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(jpeg)/Health-GettyImages-2181648348-08792564566c4c5ab3d9fa44dfd5271a.jpg)
Laser hair removal is a safe and effective option for treating hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), a chronic (long-term) skin condition caused by clogged hair follicles. The clogged hair follicles can lead to painful lumps, nodules (small masses of dense tissue), scars, and skin tunnels (wounds under the skin).
Laser hair removal can help manage HS symptoms by using a laser to emit a beam of highly concentrated light that removes the clogged hair follicles from the body.
A dermatologist (a doctor specialized in hair, skin, and nail conditions) might recommend laser hair removal as a part of your treatment plan.
By decreasing the amount of hair on the skin, laser hair removal can help reduce lumps, nodules, and abscesses that can form due to HS.
Laser hair removal can further help HS by minimizing inflammation and reducing flare-ups. It can also decrease the level of bacteria on the skin and minimize the activity of sebaceous (oil-producing) glands, both of which may worsen HS symptoms.
Laser hair removal treatment removes hair by vaporizing it. A tool emits a laser, which destroys the hair and turns it into a vapor (smoke).
There are a couple of laser hair removal techniques, and your dermatologist will recommend one based partly on the severity of your HS symptoms. HS severity is categorized into three stages:
- Hurley stage 1: Abscesses without skin tunnels and scars
- Hurley stage 2: Recurrent abscesses with tunnels and scars, along with single lesions or multiple, widely separated lesions
- Hurley stage 3: Multiple interconnected sinus tracts (abnormal channels that connect the skin to a deeper part of the body) and abscesses covering large areas of the body
Your skin tone and hair color will also factor into which of the two laser hair removal processes you receive.
Alexandrite Laser
The alexandrite laser is considered safe and effective for people with mild to moderate symptoms of HS.
The alexandrite laser has shorter wavelengths, which makes it a more effective option for lighter skin because the laser better absorbs the melanin in hair follicles. Melanin is a natural substance that determines hair, skin, and eye color.
The alexandrite laser also covers a wider area of skin, making treatment times faster and less painful overall.
Neodymium: Yttrium-Aluminum-Garnet (Nd:YAG) Laser
Although the alexandrite laser is more effective and causes less pain, the Nd:YAG laser is safer for people with darker skin tones.
The Nd:YAG laser is also more effective at treating recurring HS lesions in people with Hurley stage 1 and less advanced Hurley stage 2, two of the HS stages of severity a person may experience. The Nd:YAG laser has also been shown to reduce flares and severity of Hurley stage 1.
Laser hair removal isn’t typically recommended for more severe HS because of the severity of scarring from HS.
If laser treatment is recommended for someone with more advanced HS Hurley stage 2 or Hurley stage 3, a carbon dioxide (CO2) laser is a safer option than hair removal lasers. A CO2 laser surgically deroofs (removes the top layer) of a sinus tract.
For people without severe HS, laser hair removal is an effective and safe option to treat symptoms of HS in people of all skin tones and hair colors.
In the past, laser hair removal treatments were safe only for people with dark-colored hair and light skin. New advancements in laser technology have made the procedure safe for people with light-colored hair and light skin and people with dark skin.
Dermatologists typically perform laser hair removal sessions for HS during an in-office visit once every six weeks for several months.
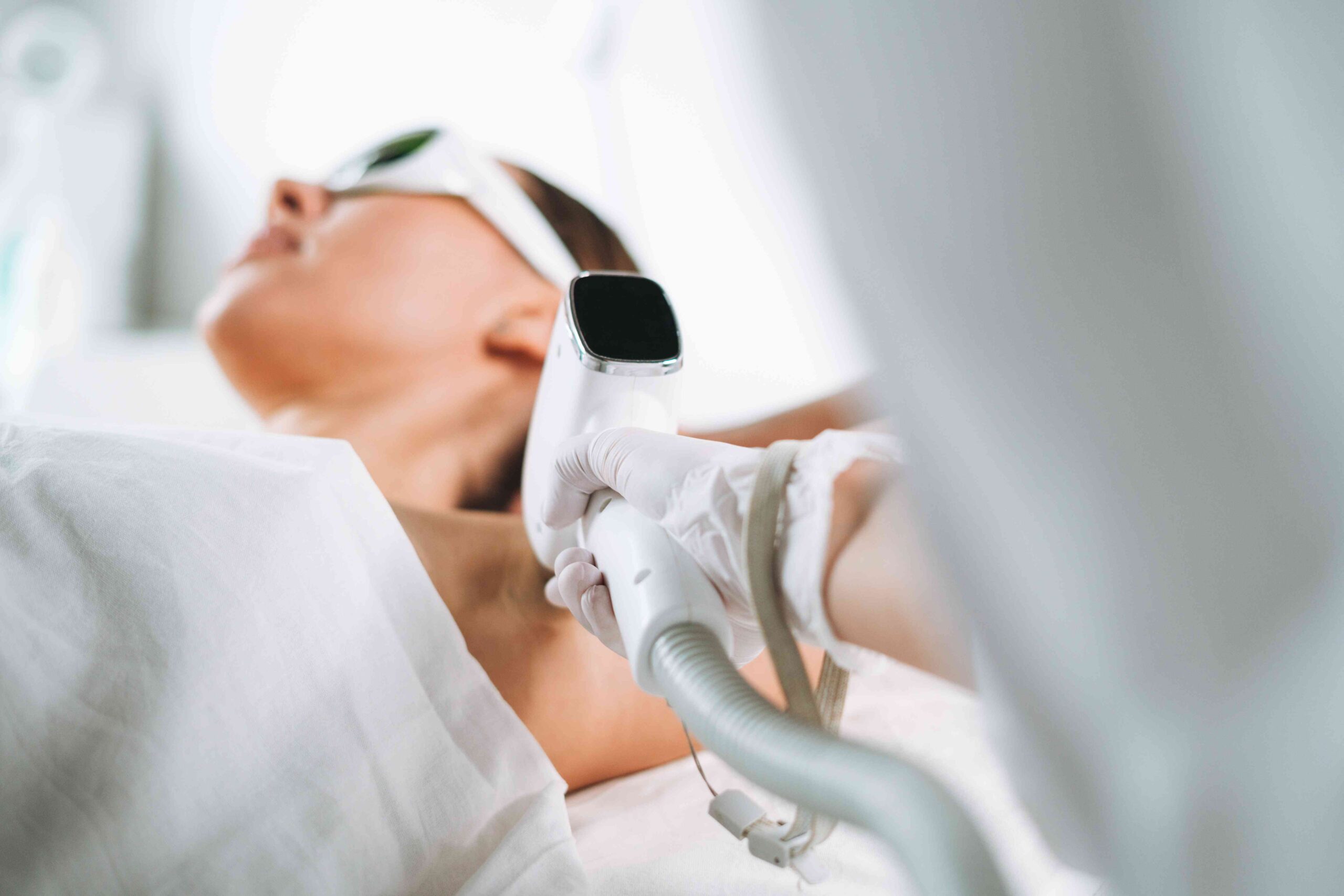
When you arrive at your appointment, your provider will apply numbing gel to the areas being treated. The gel will take approximately 30-60 minutes to take effect. You’ll then receive protective eyewear to wear during the procedure.
Your dermatologist will hold the skin tight and use a laser to treat the affected areas. The laser emits pulses that feel like warm pinpricks or rubber bands being snapped against the skin.
Treatment time can vary depending on the number of areas being treated. One area could take several minutes, but multiple or large areas may take more than an hour.
Laser hair removal doesn’t require any downtime, meaning you can return to your daily activities immediately. However, your skin may feel irritated after treatment. Your dermatologist will provide aftercare instructions to help with any potential irritation. This may include applying a cool compress at home to help relieve any redness and swelling, keeping your skin protected from the sun, and avoiding tanning beds.
Follow-up sessions are required every six weeks for several months to achieve the desired results.
While laser hair removal is a safe treatment option for HS, there are some potential risks.
Common side effects include swelling, redness, and discomfort. Rarer side effects include blisters, a herpes simplex (cold sores) outbreak, infections, scarring, and skin lightening or darkening. Rare side effects are significantly less likely if a qualified medical provider, such as a dermatologist, administers the laser treatment.
There were previously greater safety concerns for people with dark skin and people with light-colored hair and light skin, but trained providers know how to reduce safety risks in these populations.
It’s important to find a qualified healthcare provider to minimize potential risks and side effects. States may differ in requirements for who can perform laser hair removal. You should opt for someone with a medical background.
A dermatologist can be qualified and highly trained to perform laser hair removal for HS. If you have a particular provider in mind, check to see if they are licensed to practice in your state.
If you have insurance, they may also be able to recommend providers. You can ask about which dermatologists are in-network. However, insurance doesn’t typically cover the cost of laser hair removal in the United States. Sessions can be $350-900 each, depending on the area of the body and the amount of skin receiving treatment for HS.
Laser hair removal can be beneficial and safe for treating symptoms of HS. There are also a variety of other treatments for HS, including:
- Topical antibiotic: When applied to the skin, antibiotics like Cleocin (clindamycin) can treat mild cases of HS. The medications help treat infections and reduce lumps and pus-filled areas deep in the skin.
- Resinol (resorcinol) cream: This medication can open clogged hair follicles and reduce inflammation to decrease swollen, pus-filled areas, lumps, and pain. It can take about 3-4 months to see results.
- Hormone therapy: Hormone therapies include oral (taken by mouth) contraceptives containing estrogen and medications like Aldactone (spironolactone) or Proscar (finasteride). While more research is needed, evidence suggests hormones play an important role in managing symptoms of HS and that hormone therapy is an effective treatment.
- Oral antibiotic: When taken by mouth, antibiotics can decrease bacteria and inflammation, reducing flare-ups of HS on the skin.
- Biologics or biosimilars: Biologics are strong medications that target the immune system to reduce inflammation. They are effective in treating HS if other treatment options are not effective. Biosimilars are similar to biologics but usually cost less.
Your healthcare provider may recommend laser hair removal alongside one of the treatments above. They will discuss the best treatments based on your symptoms and Hurley Stage.
Laser hair removal is a relatively safe and effective procedure for treating hidradenitis suppurativa (HS). It can help improve symptoms, including lesions and scarring.
There are a couple of laser hair removal techniques for milder HS, but laser hair removal might not be the best option for severe HS. In addition to HS severity, your symptoms, skin tone, and hair color can also dictate which laser therapy you receive.
It’s important to have your laser hair removal treatment performed by a qualified medical provider, such as a dermatologist, to prevent unwanted side effects.
[ad_2]
Source link